- 작성자 Hilton
- 댓글 0건
- 조회 538회
- 작성일 2025.06.28
본문
Understanding Fascia Replacement: A Comprehensive Guide
Fascia replacement is an essential treatment in both construction and medical contexts. Whether examining its significance in structure stability or its role in assisting in recovery and healing after an injury, the subject of fascia replacement warrants extensive expedition. This post will offer a thorough understanding of fascia replacement, addressing its applications, treatments, benefits, dangers, and frequently asked questions.
What is Fascia?
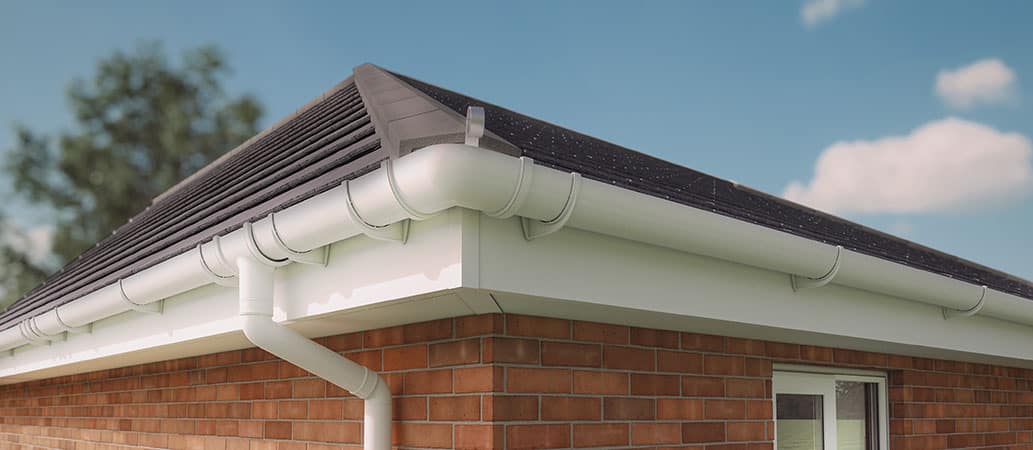
Fascia is connective tissue that surrounds muscles, bones, and organs in the body, forming an encouraging structure. In building and construction, fascia refers to the board that caps completion of rafters, serving both visual and practical functions. Regardless of the differing contexts, fascia in both circumstances serves to offer assistance and security.

Kinds of Fascia
| Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Medical | Human Anatomy | Connective tissue covering muscles, bones, and organs. |
| Building | Structure Design | Board or material covering the edge of a roof or eave. |
The Medical Context of Fascia Replacement
In the medical field, fascia replacement describes the surgical repair of harmed connective tissue. This can take place due to injuries, surgeries, or chronic conditions that jeopardize the body's structural stability. Specific conditions might demand fascia replacement, consisting of:
- Fasciitis: Inflammation of the fascia, typically resulting in discomfort and tightness.
- Muscle injuries: Severe strains or tears can harm the associated fascia.
- Surgical intervention: Procedures such as hernia repairs might need restoration of fascia.
Treatment for Fascia Replacement
Fascia replacement surgery can vary significantly based upon the underlying condition and its severity. The general steps included in the procedure typically consist of:
- Assessment: A comprehensive assessment by a doctor, consisting of imaging tests like MRI or CT scans.
- Anesthesia: The client is put under general or local anesthesia to ensure comfort during the treatment.
- Cut: A surgical cut is made to access the harmed fascia.
- Debridement: Removal of diseased or damaged tissue to prepare the site for repair.
- Fascia grafting: A graft may be collected from other areas of the body (autograft) or sourced from donors (allograft) and then attached to the location needing repair.
- Closure: The incision is sutured, and postoperative care is gone over with the client.
Advantages and Risks
Benefits of Fascia Replacement
- Restoration of Function: Correcting fascia damage can substantially enhance mobility and function.
- Pain Relief: Many patients experience minimized pain and discomfort following the treatment.
- Prevention of Further Injury: A stable structural framework assists avoid additional injuries in the future.
Dangers Involved
- Infection: As with any surgery, there is a threat of infection at the surgical site.
- Rejection of Graft: In the case of an allograft, the body may decline the transplanted tissue.
- Post-operative problems: Patients might experience complications such as blood clots or excessive scarring.
The Construction Context of Fascia Replacement
In construction and architecture, fascia serves both structural and visual functions, affecting the total appearance and energy performance of a building. Fascia replacement might be necessary when this essential part is damaged due to weather, insects, or general wear and tear.
Reasons for Fascia Replacement in Construction
- Rot or Decay: Exposure to moisture can result in wood rot, jeopardizing the structural integrity.
- Bug Infestation: Termites and other bugs may damage fascia boards.
- Cosmetic Upgrades: Home and structure owners may want to change fascia for aesthetic improvements.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern fascia boards may supply much better insulation and energy conservation.
Procedure for Construction Fascia Replacement
- Evaluation: Inspecting the existing fascia boards for damage.
- Elimination: Carefully removing the harmed fascia without impacting surrounding structures.
- Preparation: Prepping the surface area for new boards, ensuring it is clean and dry.
- Installation: Securing the brand-new fascia boards in location, guaranteeing proper positioning and sealing.
- Finishing Touches: Painting or staining to match the existing structure, if wanted.
Benefits and Disadvantages
Benefits of Construction Fascia Replacement
- Improved Curb Appeal: New fascia can considerably improve a property's appearance.
- Increased Property Value: A well-kept exterior can improve residential or commercial property value.
- Improved Protection: New fascia protects underlying structures from water damage and insects.
Disadvantages
- Expense: Replacement can be costly, especially if extensive damage is present.
- Labor-Intensive: The procedure requires experienced labor and time.
- Disturbance: The replacement process might momentarily interfere with the look and function of your residential or commercial property.
Fascia replacement, whether in a medical or building context, serves an important role in restoring structural integrity and function. Understanding the particular treatments, advantages, risks, and reasons for replacement can help individuals make informed decisions tailored to their particular requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What products are utilized for fascia replacement in building?
- Typical materials include wood, vinyl, aluminum, and composite boards.
Is fascia replacement agonizing?
- In a medical context, anesthesia is administered, decreasing pain throughout the procedure. Post-operative discomfort may differ by person.
The length of time is the healing period for fascia replacement surgical treatment?
- Healing times can vary extensively however typically range from a few weeks to a number of months, depending on the extent of the procedure and the person's health status.
Can I perform fascia replacement myself?
- While some minor repairs can be carried out by homeowners, it is advisable to hire a professional for substantial damage to guarantee security and compliance with structure codes.
How can I prevent fascia damage in my home?
- Routine maintenance, consisting of cleaning seamless gutters, inspecting for water damage and bugs, can help prevent fascia damage.
This article has actually presented a detailed introduction of fascia replacement, stressing its significance in both health care and construction. For additional queries or particular circumstances, seeking advice from a professional is constantly suggested.
댓글목록 0개
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.